Health Assessment is the process by which nurse conduct different information needed on patient condition or on particular client.
Emergency Health assessment conduct two part which are Primary survey and secondary survey.
Primary survey is or initial assessment, is designed to help the emergency responder detect immediate threats to life. Immediate life threats typically involve the patient's ABCDE, and each is correct as it is found.
Life threatening problems MUST be identified first. This is to be completed in an order of priority to ensure the most important steps are undertaken in a logical order ensuring nothing is missed. Ensure safety for yourself and any others. Do not put yourself at risk, Remove danger or move the patient.
Find out what has happened from witnesses if possible.
Secondary survey first nurses A focused history and physical exam should be performed after the initial assessment. It is assumed that the life threatening problems have been found and corrected. If that process involved CPR you may not get to this stage.
Primary Survey (ABCDE) consist rapid examination, life-threatening injuries, treat as you find.
Secondary Survey Consist history, detailed head to toe examination, all injuries, special Investigations if available.
Primary survey(ABCDE) Nurse focus on Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, And Exposure.
On the Airway Nurse should focus on check airway clearance is it blocked or not? Check head position. oxygen from the air to flow to and from the lungs, the upper airway must be unobstructed (must be clear). Once an obstructed airway occurs, the brain will develop an oxygen deficiency resulting in unconsciousness. Death will follow rapidly if prompt action is not taken.
Source of obstruction in Airway may be Bad position of neck (hyper-flexion), Collection of secretions, Tongue aspiration, Foreign body.
On the upper airway obstruction can occur because the casualty tongue falls back into his throat while he is unconscious as a result of injury, cardiopulmonary arrest, and so forth. (The tongue falls back and obstructs, it is not swallowed.), Foreign bodies become lodged in the throat (chocking), Aspiration (of regurgitated contents from the stomach, of Blood clots which may form as a result of head and facial injuries), Trauma to jaw, head and neck, swelling, bleeding, hematoma, chest injuries, open wounds to neck.
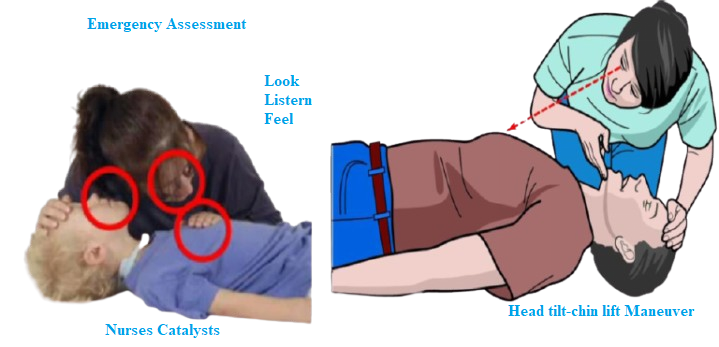
Nurse should use the Listen, Look and Feel Technics.
Check airway if it is clear with “LOOK, LISTEN & FEEL TECHNIQUE” (this term Clear means no obstructions, no secretions, it is not blocked).
Place your ear on the person’s mouth to LISTEN if he/she is breathing normally, Look to the chest of the person to see if the chest of the person can move up and down (‘observe chest movements’), Feel the breathing – feel the person is breathing.
If you do not see, hear and feel that the person (victim) is breathing, maybe the airway is obstructed, ‘blocked’. so you need to open the airway.
On the Breathing Nurses should consider that After ensuring that airway is clear, you move on the breathing. Even though the airway is not clear the victim may also not breathe for many reasons. Assess for rise and fall of chest, Respiration Rate, and depth, Look, listen and feel by watching the chest and placing your cheek a few inches above the mouth of the victim to sense any movement of air, If the victim is not breathing, they may need their head repositioned.
Remember that if the person is not breathing, no air is entering in the lungs, no oxygen is getting in the blood, and as a result organs are deprived from oxygen.
On the Circulation Nurses Should consider all matters of the blood particularly blood flow to the brain. Assessing circulation, Look for obvious bleeding
Palpate pulse: are they normal, weak or strong? The best place to check for a pulse is the carotid artery along the side of the neck along the windpipe. If there is not a pulse, then this person needs CPR. Inspect skin: is the color normal? Is it warm or cold? Clammy or dry? Obtain Blood Pressure and
Check for Hemorrhaging, If the victim is bleeding, then provide the necessary care.
Check for shock.
If signs/symptoms of shock are presented, stop the evaluation and begin treatment of shock immediately.
The signs and/or symptoms of shock include:
Sweaty but cool skin (clammy skin), Paleness of skin, Restlessness or nervousness, Thirst, Loss of blood (bleeding), Confusion (does not seem aware of surroundings), Faster than normal breathing rate, Blotchy or bluish skin, especially around the mouth, Nausea and/or vomiting.
On the Disability Nurses should assess Level of Consciousness by using score Glasgow Coma Scale, AVPU(A: alert, V: responds to verbal stimulation, P: responds to pain, U: unresponsive) Also assess pupils for equality and reactivity.
On Exposure Nurses should Completely undress the patient to facilitate thorough inspection, Maintain body temperature (warm blankets).
Secondary Survey
This part should started after stabilizing the patient condition nurses will start with History taking, Vital signs, Physical examination ( Head to Toe or system by system approach), Investigations: laboratory exam and imageries.
If patient responsive, ask about SAMPLE (Symptoms, Allergies, Medications, Past medical history, Last oral intake, Events related to injury/condition)
If patient unresponsive, try getting information from family member or transport team.
Perform Head to Toe assessment
Begin with patient lying supine, consider all surfaces/structures, inspect, palpate, auscultate. If safe (spine stabilized), turn patient to prone position and assess posterior surfaces.
Remember to do Reassessment.
Across the room observation, is the patient stable?, identification of condition(s) requiring immediate attention, uncontrolled hemorrhage, breathlessness, shock, Hypothermia, Other life threatening condition.
Always Remember to monitor vital sign as indicator of Change in the Body and Catalyst for changing patient Condition.