How drug Affect Autonomic Nervous System?
Nervous System is Complex System that are made by Central Nervous System(CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System(PNS).
Central Nervous System(CNS) Consist the brain and Spinal Cord while the Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) consist
Motor and sensory Neuron.
to understand well the Drug Affecting Autonomic nervous system you have to understand clear Anatomy and physiology of CNS.
The nervous system has two major divisions:
The central nervous system (CNS) It consists of the brain and spinal cord which play crucial role of receives and processes information and It initiates action. It Receives and processes sensory information; initiates responses; stores memories; generates thoughts and emotions. Brain (receives and processes sensory information; initiates responses; stores memories; generates thoughts and emotions. Spinal Cord (conducts signals to and from the brain; controls reflex activities).
The peripheral nervous system it consists of all nervous tissue outside the CNS, including sensory and motor neurons. it play crucial role of Transmits signals between the CNS and the rest of the body. Consists of Motor and sensory neurons. Motor Neurons (carry signals from the CNS that control the activities of muscles and glands). Sensory Neurons (carry signals to the CNS from sensory organs).
Motor Neurons consist different part which are
Somatic Nervous System (controls voluntary movements by activating skeletal muscles)
Autonomic Nervous System (controls involuntary responses by influencing organs, glands, and smooth muscle). It consists of
Sympathetic Division (prepares the body for stressful or energetic activity; “fight or flight”) which includes Adrenergic Receptors (Alpha & Beta)
Parasympathetic Division (dominates during times of “rest and digestion "and directs maintenance activities) which include Cholinergic Receptors.
Neurotransmitters.
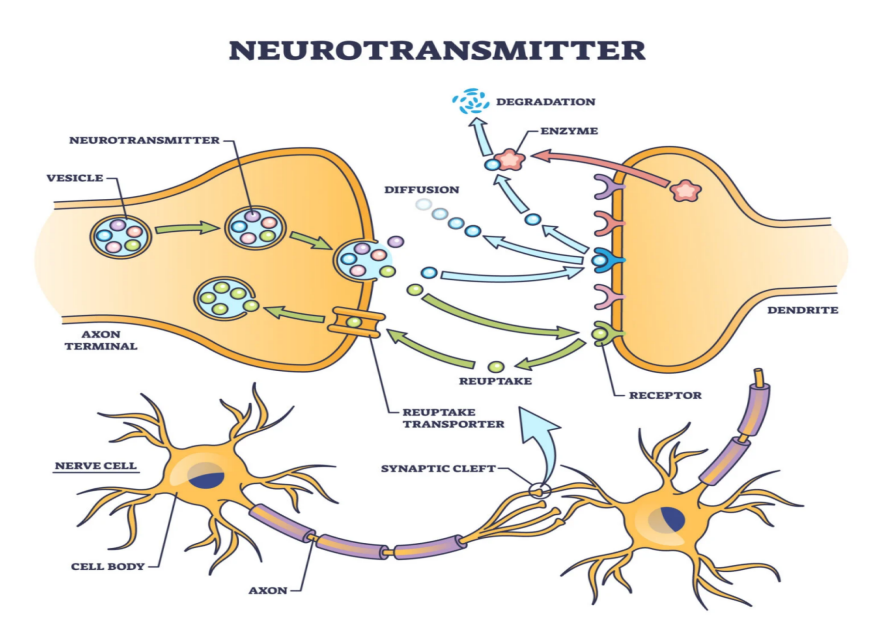
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between nerve cells, or neurons. These messengers travel across a tiny gap called a synapse, enabling signals to pass from one neuron to the next.
Unlike direct contact, neurotransmitters bridge this synaptic gap to relay signals to or from the central nervous system (CNS). Released from synaptic vesicles, neurotransmitters play a vital role in modulating and balancing neural signals, thereby maintaining brain function.
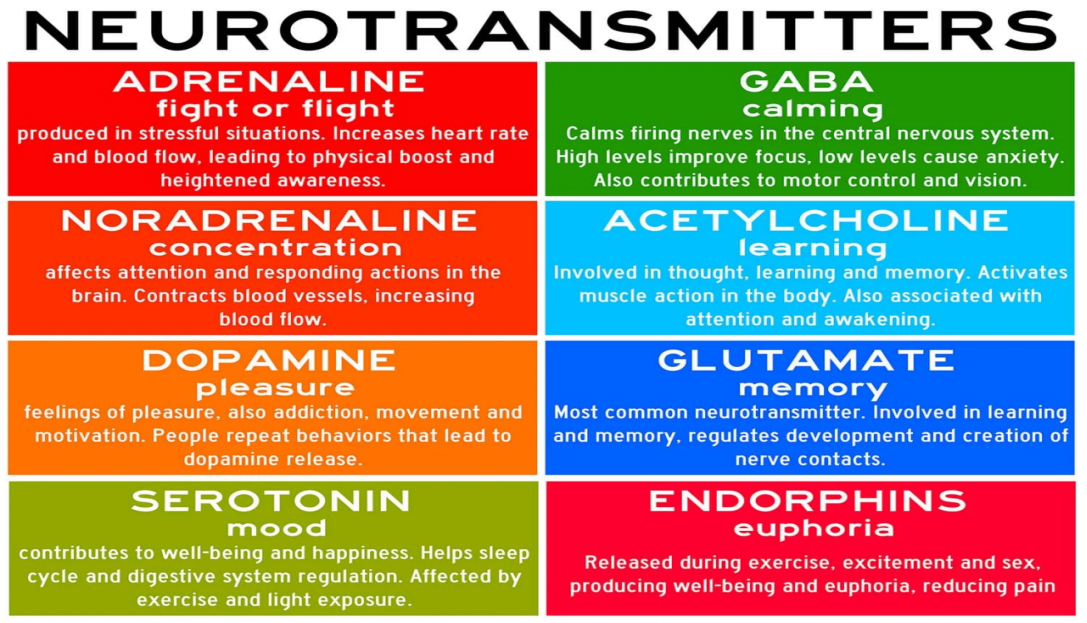
They regulate autonomic responses like breathing and heart rate and psychological functions such as learning, mood, fear, pleasure, and happiness.
Some neurotransmitters, like serotonin, have an inhibitory effect, making neurons less likely to fire, thus promoting calmness and sleep.
Others, like adrenaline, have an excitatory effect, increasing the likelihood of neuron firing and elevating alertness or arousal.
Example of neurotransmitter
action potential is the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
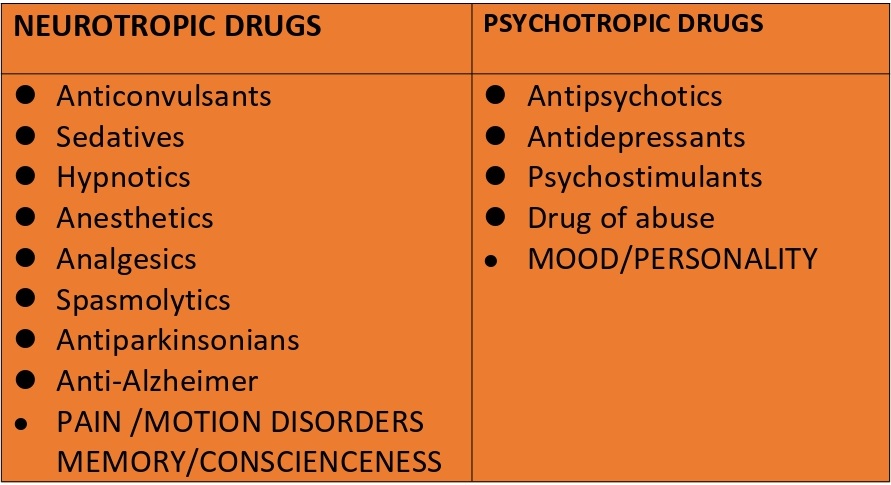
Drug that affecting Central Nervous system are Classified into Neurotrophic drugs and psychotropics Drug.
Example of Drug that affect Central Nervous system.