Introduction to Biochemistry
Biochemistry( The chemistry of life) is the study of chemical substances and vital processes occurring in living organisms it delves into the molecular basis of life, examining the structure, function, and interactions of biomolecules such as protein, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Biochemistry And Metabolism.
biochemistry and metabolism are intertwined fields that delve into the chemical processes within living organisms. biochemistry focus on the molecular composition and interaction of biological molecules, while metabolism explores the intricate network of chemical reactions that sustain life.
key areas of biochemistry
1. Molecular biology: explores the structure and function of DNA, RNA and proteins and how they interact to control cellular processes.
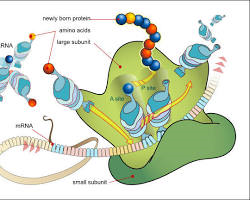
2. Enzymology: Studies enzymes, biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions within cells.

3. Metabolism: Investigates the complex network of chemical reactions involved in energy production, biosynthesis, and degradation of biomolecules.
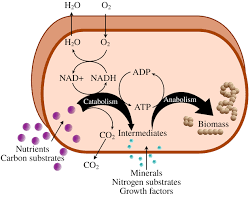
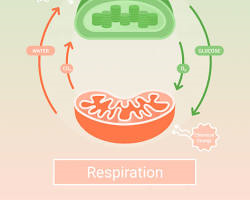
4. Bioenergetics: Examines the energy transformations that occur in living systems, including photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
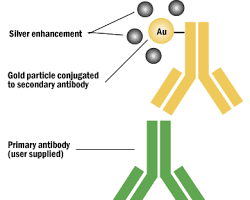
5. Immunochemistry: Explores the molecular basis of the immune system, including antibodies and antigens.
6. Neurochemistry: studies the chemical processes involved in the nervous system, including neurotransmitters and receptors. Metabolism:
The chemical basis of life
Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reaction that occur within a living organism. It involves to major processes:
A. catabolism: The breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy.
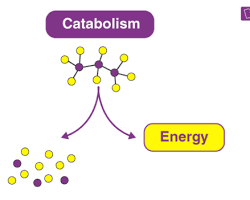
B. Anabolism: the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy.
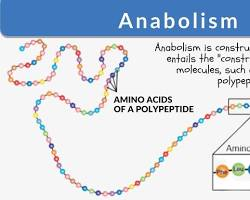
Metabolic Pathways.
1. Glycolysis: The breakdown of glycose to produce ATP.
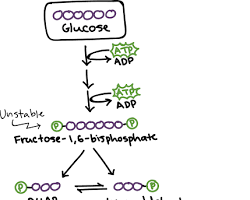
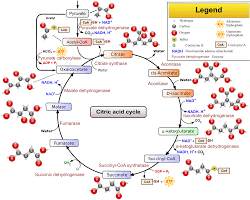
2. Citric Acid cycle( Krebs cycle): A series of reactions that oxidize acetyl-CoA, producing ATP and equivalents.
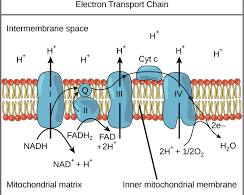
3. Electron Transport Chain: A series of protein complex that transfer electrons, generating a proton gradient used to produce ATP.
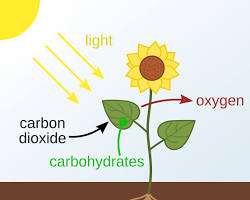
4. Photosynthesis: The process by which plants convert light energy, producing glucose and oxygen.
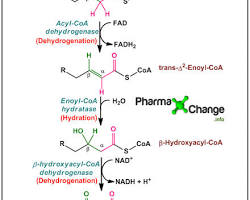
5. Fatty Acid Oxidation: The breakdown of fatty acids to produce acetyl-CoA.
6. Amino Acid Metabolism: The synthesis and degradation of amino acids.
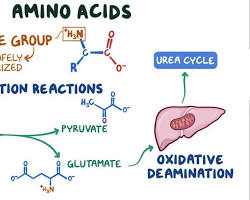
The Interplay of Biochemistry and metabolism
Biochemistry and metabolism are closely intertwined. biochemical principles provide the foundation for understanding the mechanisms of metabolic pathways. metabolic processes, in turn, are essential for maintaining cellular function and homeostasis.
Biochemistry and metabolism are fundamental to understanding the complexities of life. by by studying the molecular basis of biological processes, scientists can gain insights into health disease and the development of therapies