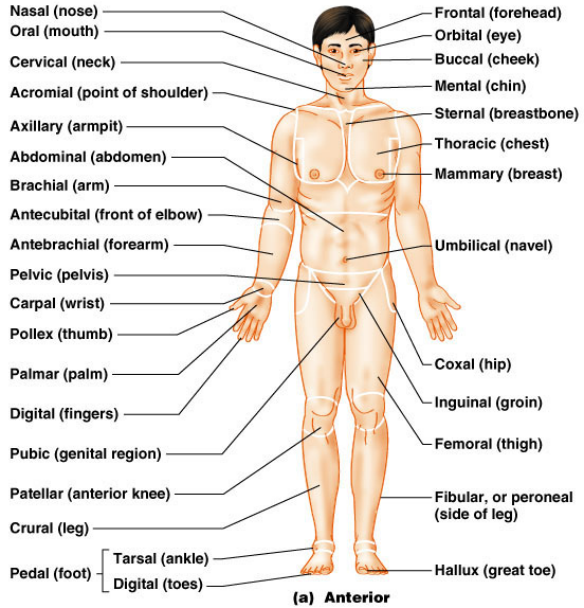
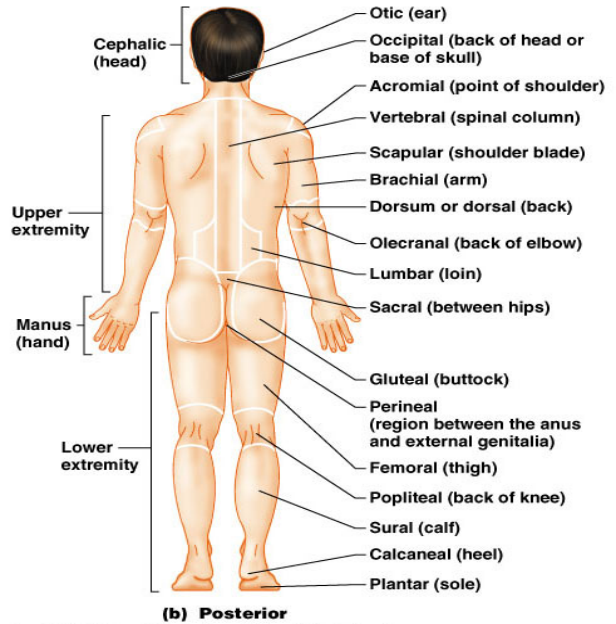
How Abdominal is divided in different Region , What are Different Anatomical Position.
Anatomy is the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another.
Physiology is the study of the function of the body’s structural.
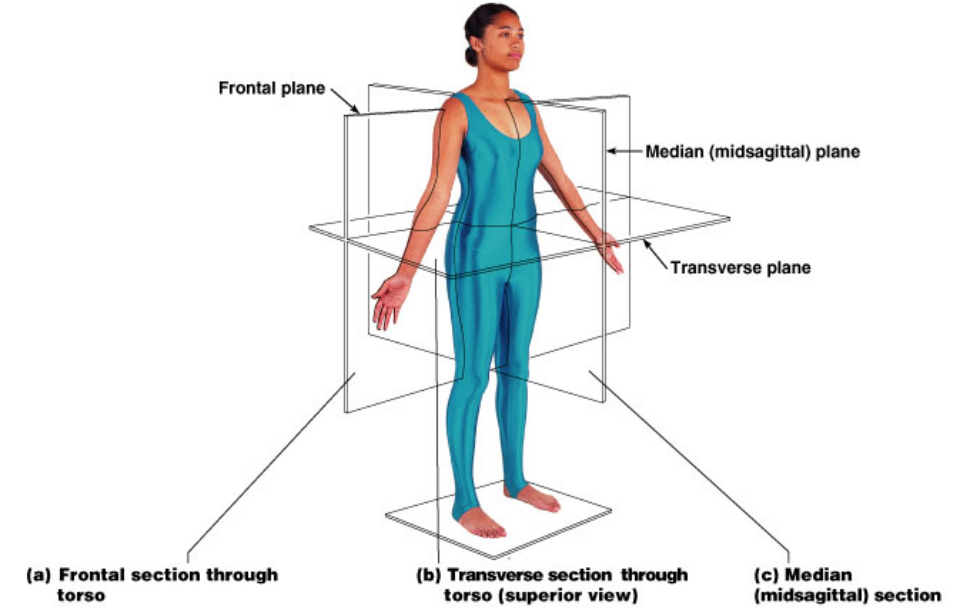
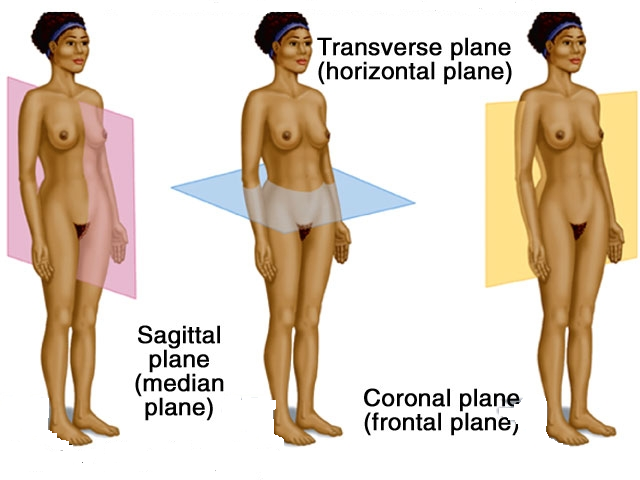
when the body is :
- Body erect
- Feet slightly apart.
- Palms facing forward .
- Thumbs point away from body.
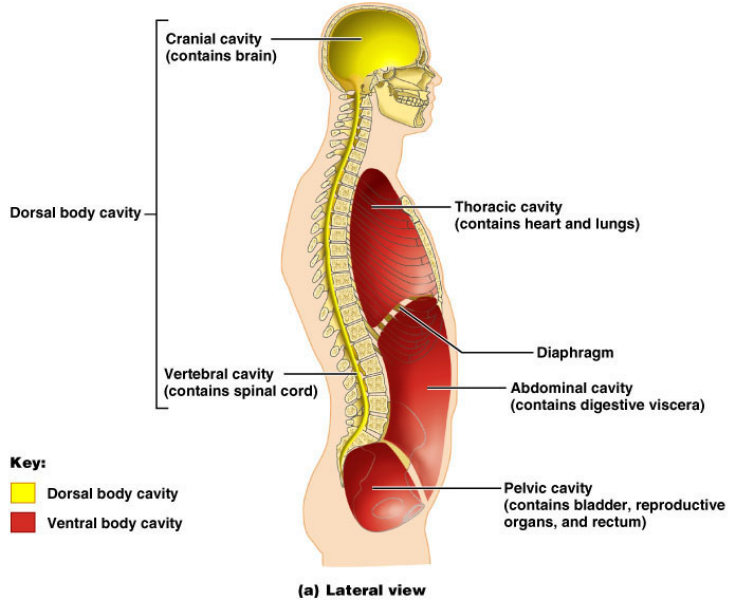
1. Cranial Cavity:
- Location: Inside the skull (cranium)
- Contents: Brain, meninges (protective membranes), cerebrospinal fluid
- Function: Protects the brain, which is a vital organ for thought, movement, and sensation.
2. Vertebral Cavity:
- Location: Within the vertebrae (backbones)
- Contents: Spinal cord, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid
- Function: Protects the spinal cord, which is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
B. Ventral body Cavity
1. Thoracic Cavity (Chest Cavity):
- Location: Between the neck and diaphragm
- Contents: Lungs, heart, thymus, trachea, esophagus, major blood vessels
- Function: Houses and protects vital organs like the lungs and heart.
2. Abdominal Cavity:
- Location: Below the diaphragm and above the pelvis
- Contents: Liver, gallbladder, pancreas, stomach, intestines, kidneys, spleen
- Function: Contains many digestive organs, as well as the kidneys, spleen, and other important structures.
3. Pelvic Cavity:
- Location: Within the pelvis
- Contents: Bladder, rectum, reproductive organs (uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes in females; prostate, seminal vesicles, vas deferens in males)
- Function: Houses the organs of the urinary and reproductive systems.
4. Mediastinum:
- Location: Within the thoracic cavity, separating the lungs
- Contents: Heart, thymus, trachea, esophagus, major blood vessels
- Function: Provides support and protection for the heart and other vital organs in the chest.
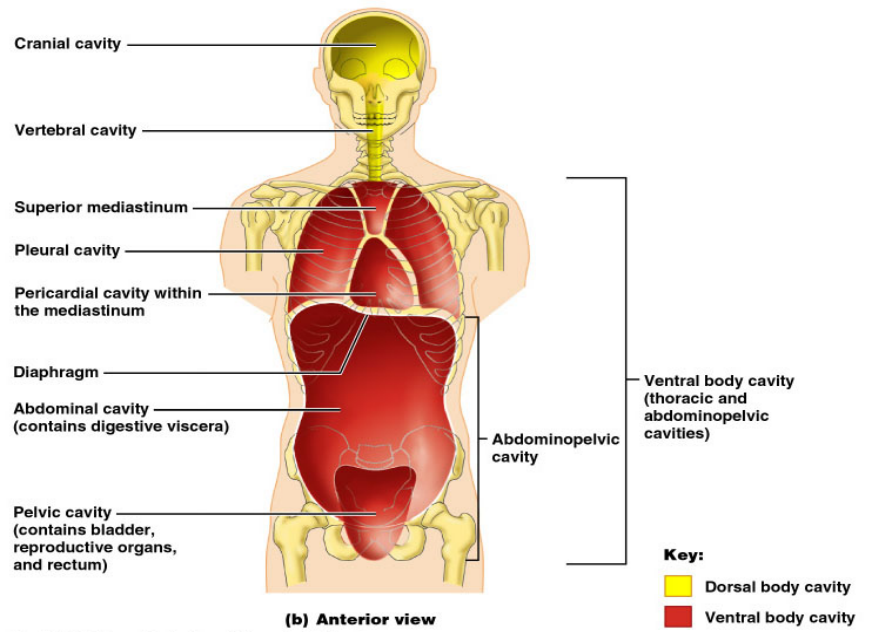
- Thoracic cavity is subdivided into pleural cavities, the mediastinum, and the pericardial cavity
- Pleural cavities each houses a lung
- Mediastinum contains the pericardial cavity, and surrounds the remaining thoracic organs
- Pericardial cavity encloses the heart
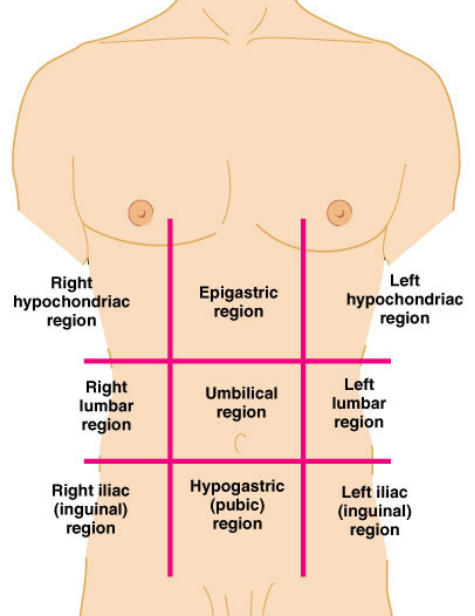
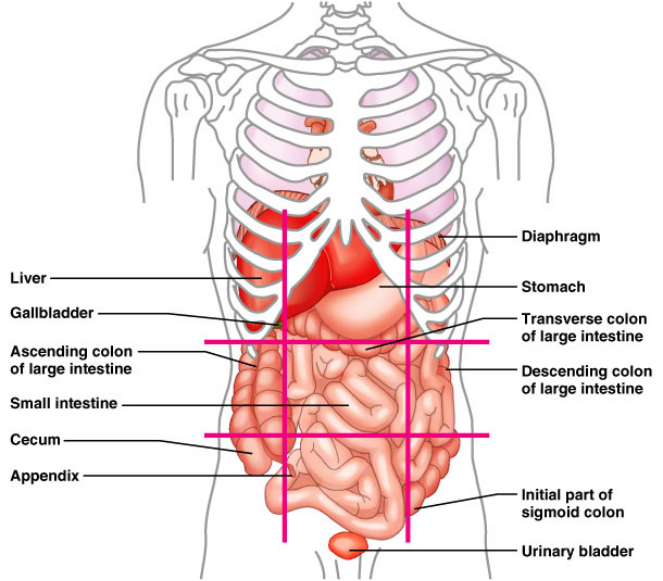
Abdominal pelvic cavity contain different part such as 9 region of abdomen.
- Umbilical
- Epigastric
- Hypogastric
- Right and left iliac or inguinal
- Right and left lumbar
- Right and left hypochondriac
Abdominal pelvic quadrat
- Right upper (RUQ)
- Left upper (LUQ)
- Right lower (RLQ)
- Left lower (LLQ)
Level of Organism
1. Chemical Level: This is the most basic level, where atoms and molecules come together to form the building blocks of life. Examples of chemical components include proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and water.
2. Cellular Level: Cells are the smallest units of life and are composed of various chemical components. They can be specialized to perform specific functions, such as muscle cells for contraction, nerve cells for transmitting signals, and blood cells for transporting oxygen.
3. Tissue Level: Tissues are groups of cells that have a similar structure and function. There are four main types of tissues: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue.
4. Organ Level: Organs are composed of multiple tissue types working together to perform a specific function. Examples of organs include the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and brain.
5. Organ System Level: Organ systems are groups of organs that work together to accomplish a particular task. The human body has eleven major organ systems, such as the circulatory system, respiratory system, digestive system, nervous system, and endocrine system.
6. Organism Level: The highest level of organization is the organism itself, which is a living individual composed of multiple organ systems working together to maintain life.
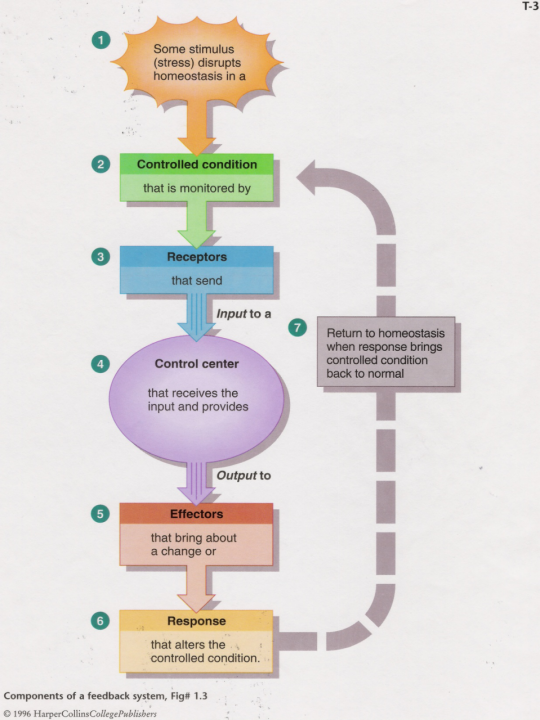
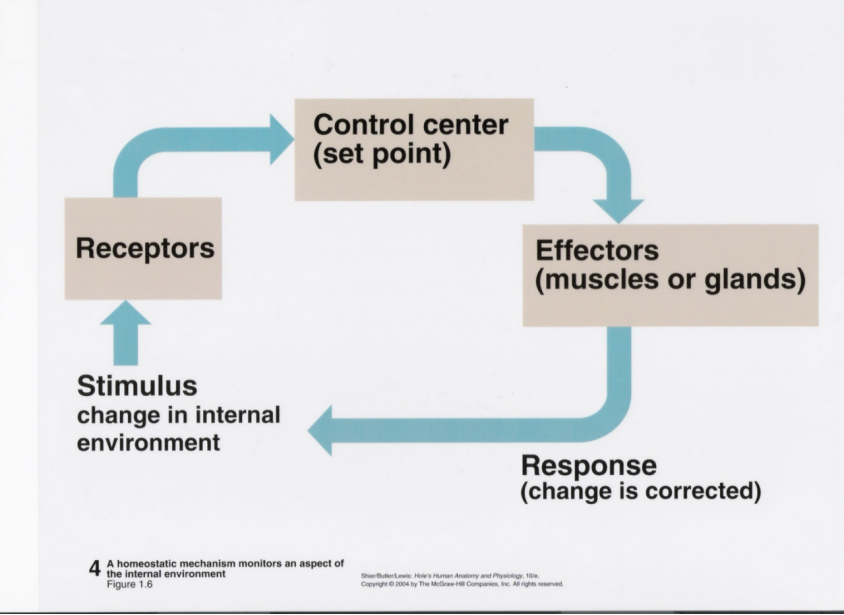
Homeostasis and feedback
Homeostasis means maintaining a fairly constant internal environment in spite of a changing external environment.
All body systems attempt to maintain homeostasis.